In each case, the thickness of the floor screed is determined individually. On the one hand, its height should be sufficient to achieve the required characteristics of the strength of the base. But with another layer of the mixture to be poured, I always want to reduce it as much as possible in order to reduce costs. Also, the characteristic features of the room where the rough coating is arranged here have a considerable influence.
Primary requirements
There is no single and ideal value in determining the height for the created floor screed. The choice of this parameter depends on many factors. For each room, it is selected individually in accordance with the purpose of the room and the degree of unevenness of the base.

Application of screeds indoors
The thickness of the floor screed under the finish coating is determined by:
- type of flooring or soil composition,
- financial resources available
- selected for pouring mixtures, waterproofing, reinforcement option and other materials used during installation,
- requirements for heat and sound insulation,
- the presence of certain irregularities on the base located under the screed,
- the need to organize a bias to one of the walls or the exit,
- the need to fill in the pipes of the "warm floor" or other communications.
These ebbs for windows in size are easy to choose. They should only overlap the existing lower slope in the wall opening. In the case of a screed on the floor, you will have to take into account much more points.

In apartments and residential premises, a thin screed is mainly used.
SNiP recommendations
Building codes give only recommended numbers. For example, the minimum thickness of a DPS screed should be 20 mm. But this is a variant of the floor without a reinforcing mesh, heat-insulating substrate and communications. If reinforcement is done or insulation is laid from below (expanded clay is poured), then it will not be possible to manage with 20 millimeters. The layer height will come out much more.
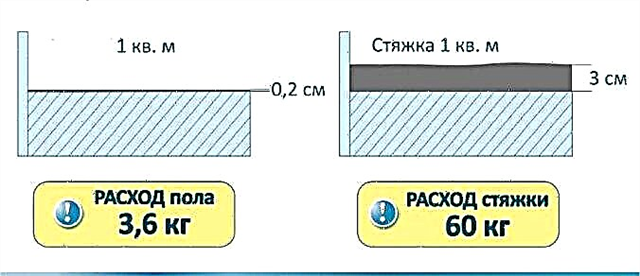
Material consumption depending on screed thickness
The main requirement of SNiPs for the "rough floor" is strength. If it is made of DSP, then such a layer must withstand at least 150 kg / cm2. If gypsum mortar is used, then the hardness index can be reduced to 100 kg / cm2.
However, when pouring self-leveling polymer compositions on top, the bottom floor screed will have to be made with a strength of at least 200 kg / cm2. Such polymer blends quickly set, creating a strong internal stress. They can simply tear off a not too strong screed from the base. From the above requirements, one should proceed from when calculating the thickness of a rough coating based on cement or gypsum.

Minimum thickness
According to building codes, the minimum screed thickness should be as follows:
- when using fine-grained sand concrete without reinforcement and insulation substrates - 20 mm,
- in the presence of heat-insulating materials under the screed - 40 mm,
- for water floor heating - 45 mm plus the diameter of the pipes.

minimum allowable screed thickness
A thicker layer is allowed. But if the height of the screed is less, then it will not be able to provide the proper strength. Then add concrete on top a little extra will not work. In this case, the coating will delaminate. If the adjustment of the plastic windows still allows you to fix something in them after installation, then the concrete or gypsum monolith on the floor should be poured all at once.

Cons of thin screed
Maximum screed thickness
The thickness of the screed to the maximum of the norm is not regulated at all. The concrete layer is allowed to be made arbitrarily thick. Moreover, if it is performed with a height of more than 100 mm, then reinforcement must be provided without fail. It can be a grid for a coupler of a floor or fiber.
The main limitation on maximum thickness is money. The thicker the rough layer, the more building materials in it and the higher its price. Make this coating too thick is not worth it. Estimated costs will come out considerable, and there will be minimum benefits. Plus, with the height of the concrete layer, its mass grows, the interfloor overlap may not be able to withstand excess weight.
Also, do not pour concrete screed over water-heated floor pipes with a thickness of more than 25-30 mm. So it will take in too much heat. The underfloor heating system will have to spend the excess heat energy on heating the concrete, instead of returning it directly to the indoor air.

Screed thickness for different sexes
Permissible sizes for different types of screed
According to the thickness of the screed, rough coatings are conventionally divided into:
- Thin - from 2 to 7 cm.
- Thick - from 7 to 15 cm.
Layers of less than 2 centimeters are usually made of self-leveling compounds and do not relate to screeds, but to bulk floors. And the thickness of more than 15 centimeters is already more than concrete floors with reinforcement.
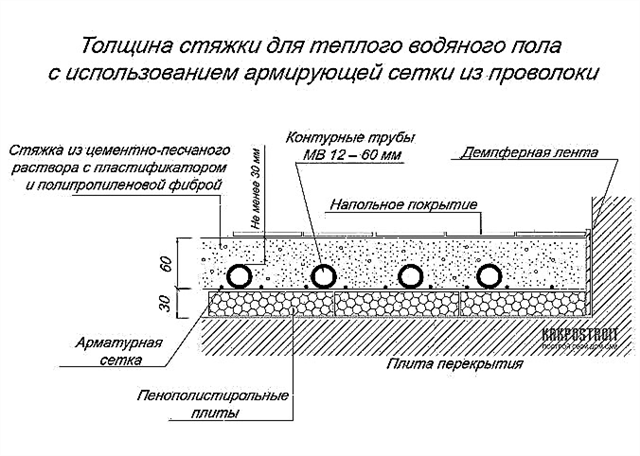
Design features of screed under floor heating
Features of arranging a thin floor screed
Thin screeds are used in rooms where there will be no strong chiseled loads during floor operation. Usually these are kitchens, living rooms, bedrooms and other living rooms. A layer of 20–50 mm will suffice here. For corridors and bathrooms, 50–70 mm are already recommended.
Such screeds are poured and leveled literally in one day. Then you still have to wait a few days before the concrete sets. But the very work of preparing the base and mixing the solution, as well as pouring the mixture, is carried out as soon as possible.

Sand concrete consumption per m2
Features of arranging a thick screed
Thick screeds are used in places with a higher mechanical load on the floor. Often they are poured not so much for leveling the floor, but for the sake of obtaining a reliable foundation for this or that equipment. And in fact, it is always always a concrete mix with reinforcement with steel bars. Gypsum solutions are of little use here.
Thick floor screeds are installed in:
- utility rooms
- house boiler rooms,
- garages
- baths, etc.
In this case, the terms and time for concrete pouring, and waiting until the floor is ready, are increased. A thick layer of concrete gains hardness obviously longer than a thin one. At the same time, you still have to spend time carefully reinforcing the concrete layer with reinforcement. Without it, such a screed will necessarily crack when hardening and will quickly become worthless.
How to calculate the amount of material for different types of screed
Conclusion
Too far to depart from the minimum thickness indicated in SNiPs for a particular case is only in extreme cases. These dimensions of the layer are selected in such a way as to provide the necessary strength and wear resistance of the screed, but at the same time minimize the cost of its arrangement.
If the floor is made in a room with high humidity or with heavy loads on the coating, then the concrete will have to be poured thick and reinforced inside. But in residential premises of apartments it is recommended to make a screed with a minimum permissible thickness so as not to overload the floors too much and not to spend extra money.
Features of screed application
There is no single concept of how thick the screed should be, since this parameter depends on a number of conditions:
- from the type of flooring of the building,
- by type of soil
- from the purpose of the room.
All of the above factors affect not only the indicator, what will be the thickness of the cement-sand screed, but also on:
- cost of work,
- to choose a particular brand of cement,
- the type of reinforcing mesh used.

Based on the height of the concrete layer poured, the screed is:
Minimum thickness - up to 20 millimeters. This type is equipped without the use of reinforcement. Self-leveling mixtures are most often used for pouring screeds.
Medium thickness - up to 70 millimeters. In this case, a reinforced network or reinforcement is used.
Maximum thickness - up to 150 millimeters. This type of screed can be called a monolith with reinforcement. Usually, this option for the home is both the foundation and the floor, combined into a single system.
The thickness of the concrete screed largely depends on the building materials that are planned to be used in its arrangement. For example, a layer of concrete with crushed stone cannot be the minimum thickness.

For pouring thin screeds, the best choice is a self-leveling mixture designed for finishing the floor for installation of the coating. With its help, a thick and perfectly even layer is obtained - after it has completely dried, they proceed to the installation of decorative material.
There are some nuances regarding determining the thickness of the screed when it is planned to install a warm floor. Given the diameter of the pipe for the heating system, and it usually does not exceed 25 millimeters, a 50-70 mm solution layer will suffice.
At the same time, experts believe that for optimal functioning of the structure and good heating of the rooms, a 4-centimeter thick concrete above the pipeline is enough.
If a higher floor screed is performed, the layer thickness will significantly complicate the adjustment of the supplied heat, since most of the energy will be spent on heating the concrete.
Minimum screed height
According to the SNIP, the minimum floor screed thickness is 20 millimeters. But one feature should be noted. Depending on the material used, the height of the concrete layer may be different. If a screed is created on the basis of metal cement, then two centimeters is quite enough.
When it is not planned to install a reinforcing mesh, then the minimum thickness cannot be less than 4 centimeters. This is explained by the fact that a lower layer height will not provide sufficient strength and wear resistance of the coating (in more detail: "What is the minimum floor screed layer you can do").

To install screeds with a minimum thickness, several conditions must be met:
- the presence of a rough floor,
- screed-lined surface
- lack of pipes or fittings.
A thin layer of concrete screed is not made in rooms for technical purposes and where there is an increased load on the floor surface.
The thickness of the floor screed in the apartment, namely in the kitchen, in the hallway and bathroom cannot be minimal, here experts recommend laying as thick a base as possible.
Arrangement of thin screed
Typically, the minimum thickness of the concrete screed is used where leveling is required.
The sequence of work on flat ground is as follows:
- Pour crushed stone (gravel) and sand with a layer, level it and carefully compact it.
- A layer of waterproofing material is laid on top, which can even be a simple film of polyethylene.
- Then a reinforcing mesh is placed and simple aluminum beacons mounted on a gypsum base are mounted (more: "Reinforcing mesh for floor screed - types and methods of use"). They are fixed in increments of 100-150 centimeters parallel to each other.
- Concrete mixture is poured.
The minimum screed height using reinforcement cannot be less than 4 centimeters. Due to the presence of the mesh and the small thickness of the layer, concrete is used, made with the addition of fine gravel.

As a result of compliance with this technology, despite the fact that the solution is poured in a thin layer, the leveling screed of the floor whose thickness does not exceed 40 millimeters is reliable.
In order to enhance the strength of the coating, cement of a grade not lower than grade M 300 should be used and special plasticizers added to the mixture.
To mix the mortar, one part of cement and four parts of gravel and sand are taken. The components are thoroughly mixed together to a uniform mass. It is best to use a small volume mixer to prepare the mixture.
Start to fill the screed in the direction from the wall to the door. There is no need to immediately lay out all the concrete, and this is according to technology and should not be done.

The solution must be poured according to the following scheme:
- in width - meter,
- in length - from one wall to another,
- using the rule, conduct along the beacons, due to which the concrete layer is leveled, while the excess mixture is removed,
- with subsequent meters of concrete, the procedure is repeated.
Screed maximum height
There is no exact definition of what the maximum thickness of the screed should be. The fact is that for each individual case, this parameter has its own valid values.
Experts are of the opinion that it makes no sense to make a screed with a thickness of more than 17 centimeters. It is not always necessary to make a concrete structure with reinforcement 150-170 millimeters high.

A significant thickening of the layer is done only in some cases:
- if the foundation is being prepared, which will simultaneously become the floor. In such a situation, a monolithic 15-centimeter screed is an integral element of the supporting structure,
- in the case of arranging the floor surface in a room with a high load, for example, in a car workshop. The car has a lot of weight and its impact on the floor is significant, so the creation of a screed with a height of 15 centimeters is quite justified,
- when laying the floor on problem soil.
Sometimes builders suggest increasing the thickness of the screed to hide the presence of significant differences in height. But defects in the original surface can be eliminated in other ways.
Before equipping a screed with a height of 15 centimeters, experts advise to consider the possibility of using other options to level sharp changes in the heights of the rough foundation. You can try to eliminate significant defects with the help of a jackhammer, as well as using crushed-sand composition or expanded clay.
In the case when it is possible to fix the defects using these methods, there is no need to fill the concrete with a 15-cm layer.

It is necessary to take into account such a moment: in the presence of serious differences, if they are eliminated only using concrete mortar, the amount of expenses will be significant. Most often, such cash costs will not be justified. The fact is that arranging a screed of great height requires a huge consumption of concrete.
Also, laying the maximum layer of the solution during the installation of a warm water floor is not financially justified. A significant thickness of the concrete screed above the pipes with a coolant will lead to slow heating of the floor surface. The effectiveness of such a design will ultimately be insignificant, and heating costs will increase to enormous numbers.
For this reason, it is important to know how to calculate the thickness of the screed correctly (in more detail: "How to calculate the floor screed - how many materials are needed"). Based on the result, you can determine the amount of required materials.
What materials are the screed used for?
The most popular is concrete pouring. When applying it, you need to remember a few points. Since the preparation of the solution requires not only sand and water, cement should be purchased at least M 300.
If the fractions of building materials do not exceed 3-5 millimeters, the required quality of the final coating will be ensured. Also, the final result will have a positive effect on the use of not sand, but its screening, since the adhesion of the particles will improve.
In order to improve the quality characteristics of the floor to be installed and to eliminate the possibility of screed destruction in the future, plasticizers should be poured into the cement mortar, which are special additives that increase the strength and plasticity of the concrete layer.
It is especially necessary to use plasticizers when mixing mortar in the case of thin filling of the floor surface.
Bit of theory
Screed is considered one of the elements of building structures, the creation of which is mandatory if you want to get a strong and durable flooring. Other solvable tasks of a somewhat specific class include improving thermal insulation performance and even waterproofing.
The two main functional tasks of the screed are surface leveling and load distribution. In the first case, the specific value of the thickness of the screed for the floor will be made - depends on the existing configuration of the surface of the floor and room, geometry and elevation. Note that the minimum figure using modern materials is only 3-5 mm.
The second task is to ensure load distribution, which directly depends on the strength of the layer. Norm, what thickness the floor screed should be - does not exist. There is an exact requirement for technical indicators: the coating layer must withstand 15 MPa in compression and have a slope of no more than 0.2%.
The screed corresponding to these parameters can be made of:
- cement-sand mixture with a proportion of materials 1: 3, which is a classic option,
- modern cement-containing ready-mixed building mixtures,
- self-leveling compositions containing polymers,
- mixtures with the addition of expanded clay, perlite.
Various means are used to increase the strength of the layer. If the minimum screed thickness is more than 80 mm, it is recommended to use a steel reinforcing mesh. At lower rates - you can do with a special plastic. If the thickness of the floor screed does not exceed 4 cm, it can be strengthened with polypropylene fibers.
 Reinforcement option
Reinforcement option
How is the acceptability of a particular type of solution evaluated?
Very often in homes there are times when the minimum layer of floor screed is quite significant. This can be, for example, with the trough-like shape of the base surface, when the height difference is large and a kind of hollow forms in the center of the room. In this case, the “floor screed thickness” parameter is evaluated, including by the permissible weight in accordance with the characteristics of the floor.
To reduce weight, you can use various fillers of the mixture for the solution.
- expanded clay crumb has the best combination of high volume and low weight,
- perlite is characterized by the property of "fluffing" of the solution, increasing its volume with constant strength after solidification,
- slag and crushed stone are effective fillers, however, the layer thickness when using them should not be less than 100 mm.
With the help of modern materials, you can cope with most of the problems associated with the excessive weight of the leveling coating. For example, the original floors can form steps, troughs, the room may have a large height in the center. An excellent exit is a multi-layer screed. The thickness of the layer is formed from dusting powder, the main strength zone, and the top coating, which ensures smoothness. For each part of the structure, it is necessary to strictly follow the condition of maintaining the minimum thickness depending on the material.
Classic recipes
Let us dwell on the composition that is most applicable today - the cement-sand mixture. For its preparation, it is enough to mix the components and dilute them with water until a thick sour cream is formed. After this, the solution is stacked and leveled. The minimum thickness of this type of cement screed depends on many factors:
- height difference of the floor surface,
- room configurations
- the possibility of convenient placement of lighthouses,
- grounds for pouring.
In the average case, when forming on an even, solid foundation, the minimum thickness of the cement-sand mixture floor screed should be 40 mm. These are technical requirements specified by standards.
However, experts recommend other values. In particular, the thickness of the screed in the case of using a cement-sand mixture should be:
- not less than 70 mm when laying without reinforcing on waterproofing on wooden floors or ceilings on beams capable of deformation,
- at least 50 mm when laying on concrete slabs to prevent the rapid departure of moisture from the layer and preserve its strength,
- not less than 100 mm when using perlite or expanded clay for insulation.
These requirements can be used comprehensively. For example, to align the trough-like form of the base, the following rule is followed: the general elevation is divided into zones. The thickness of the floor screed in the apartment will consist of a powder or a layer with the addition of perlite, expanded clay to reduce weight and the upper one created using cement-sand mortar with a thickness of at least 40 mm.
The minimum layer height can be slightly reduced - German building standards allow a value of 35 mm for mixtures using cement grade 400. These figures refer to a solution with a classic additive in the form of lime milk for plasticization.
The use of modern means of plasticization based on polymers will slightly reduce the thickness of the screed - up to 30 mm. However, the cost of such consumables cannot be compared with the classic ones. Their use looks rational only in the case when you have to save literally every millimeter of the rise.
Laying in a modern apartment
Modern housing can pose a wide variety of tasks for builders.
These include:
- floors with heating system "warm floor",
- laying communications for the lower connection of radiators,
- plywood base layer flooring,
- laying on top of electric heating films,
- semi-dry screed finish,
- floor screed to cover the ground floor in houses built on the ground.
In all cases, it is necessary to strictly follow the condition for creating minimum thicknesses of screeds, so that the achieved result shows an acceptable level of strength, durability, and does not affect the characteristics of other structures and engineering networks. Although in each case the performance of the coating layer is selected individually, there are certain recommendations for certain decisions.
Laying with underfloor heating and pipe communications
There are two thicknesses for the screed, inside which is located the structure of liquid heating "warm floor".
- The total thickness is 70-80 mm.
- The minimum thickness of the floor screed located on top of the pipes is 30 mm.
When constructing a coating on underfloor heating, you can use a standard cement-sand composition or ready-mixed building mixtures of a similar formulation. The minimum thickness of 30 mm is compensated by the load distribution - the top layer is not isolated from the general structure, therefore, there are no problems with the surface strength.
In cases where for the tasks of leveling the floor or achieving high strength it is necessary to form a layer of a solution of more than 100 mm, an individual analysis of heat transfer is carried out. This is true for the location of pipes without reference to the upper level of the floor surface. If you do the styling so that the finish layer is 30 mm - no additional calculations are required.
 Water screed heating
Water screed heating
Laying on film heaters
Floors equipped with film heaters are necessarily arranged according to pre-installed thermal insulation. It can be both foamed polymeric materials and natural ones - for example, cork flooring. Widely applied solution using a raised floor from boards on logs or plywood.
To cover such a floor with a screed, the requirement for its minimum thickness corresponds to technical standards and should be 35 mm, when using reinforcement with polypropylene fibers - 30 mm. You may need to create a screed of 30 mm for laying tiles with a minimum rise in floor level. In this case, the use of polypropylene fibers or plastic mesh is mandatory.
Modern materials
The so-called self-leveling self-leveling floors are the last word in construction technologies. The composition for creating such a coating contains polymer components that simultaneously act as plasticizers and form a strong, smooth surface.
The bulk floor can be used as a final screed if you need to make a very thin layer for a minimum rise in floor level. This is written in almost all reference materials for finished building mixtures of this class.
However, in fact - the minimum floor screed thickness from a self-leveling compound should be 2 cm, with a maximum of 30 mm. This is not much more than a cement-sand layer with reinforcement, and the cost of the solution is very high.
 Self-leveling
Self-leveling
General rules for creating screeds with a minimum thickness
Ties with a minimum thickness meet industry requirements and can withstand normalized loads. The problem is that they do not have a margin of safety. Therefore, the arrangement of the laying structure is mandatory.
The list of measures includes:
- Mandatory decoupling with the base. To form a cement screed directly on the surface of a concrete slab is not recommended. The adhesion of the composition with the base will lead to the transfer of mechanical stress and cracking. Therefore, the screed is laid on the separator layer, which can be played by simple waterproofing from a polymer film,
- damping. Thermal expansion can lead to cracking of the screed of minimum thickness. To avoid such a nuisance, a damper zone is created around the perimeter of the room. The clearance must be at least 20 mm. To form this structural element, a special construction damper tape is produced. It is laid around the perimeter of the room before creating waterproofing and laying the screed.
The applicability of a material to create a screed is evaluated individually. Cement-sand mixture leads in mass per unit volume. To reduce weight, perlite and expanded clay chips are added to the solution. Lightweight ready-made building mixtures are also available, which can also be used for floor insulation. When using such compositions, it is recommended that you carefully follow the manufacturer's instructions in terms of the minimum thickness of the screed.
As a conclusion, we can note: when creating a screed of minimum thickness, one should not ignore the instructions of manufacturers of building materials and the advice of specialists. Violation of the rules necessarily leads to a decrease in the service life of the coating, cracking and other troubles.
Video of the minimum thickness of the screed - only 1 cm:
General requirements
When performing floor screed, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- At the stage of preparation of the base, it is necessary to carefully repair all cracks and holes so that the lower floors do not suffer during the pouring process, since the mixture contains water.
- Filling is prohibited in rooms with temperatures below 5 ° C, as non-compliance with this recommendation will lead to a decrease in its strength.
- The density of the screed should be the same throughout the volume. Any cracks, chips and voids inside it are not permissible.
- When laying over insulation, it is recommended to leave a gap between pouring and walls of 20-40 mm, which is filled with insulating material.
- Monolithic screeds are separated from the walls with a damper tape.

- Finishing flooring is only laid when the subfloor is completely dry (minimum drying time is 24 hours).
Advice! The light gray color of the coating is an indication that the mixture has dried completely.
- SNiP admits that the rough floor may have deviations: for parquet, laminate, linoleum and self-leveling floors - up to 2 mm by 2 meters, for other types of coatings - up to 4 mm by 2 meters.
- If the height of the screed is more than 40 mm, then reinforcement is necessary. In rooms where large loads on the floors are not provided, the absence of reinforcing components is allowed with a layer thickness of up to 70 mm.
Optimum screed thickness
How thick the floor screed should be, its type, the necessary composition of the mixture depend on the following factors:
- the presence of bumps and elevations of the base base,
- what exactly is the mixture poured onto (on a floor slab, on an insulation layer or on pipes - in the case of a heated floor),
- what coating is the surface prepared for,
- features of the room (floor loads, humidity, temperature, and so on).
Base base
The greater the irregularities and elevation, the thicker the layer of solution is needed. With minor flaws, the minimum thickness of the floor screed will be 20 mm. If you have to deal with large differences (more than 60 mm), then there is no need to talk about the minimum thickness. In this case, there is a reason to make a solution of a mixture of coarse sand, cement and water, its height will vary from 100 to 150 mm.
Advice! If you want to save on concrete mix - use expanded clay or crushed stone as a partial alignment.
If you think that you can determine the unevenness of the floor “by eye”, then do not flatter yourself: your eyesight can let you down. It is better to use a special level for this.

Classification
There are 3 types of screed depending on its thickness.
The first type is a thin, rough floor. Self-leveling mixtures are used to fill it, which allows you to create a layer up to 20 mm. In this case, there is no need for reinforcement.
The second type is a screed up to 70 mm high. In this case, reinforcement from a metal mesh or reinforcement bars is necessary.
The third type is a layer of maximum thickness up to 150 mm, which is a monolith with internal reinforcement.

The composition of the mixture for screed
With irregularities and height differences less than 20 mm, it is better to use self-leveling mixtures, with which you can achieve an even and thin layer. After drying, you can immediately put on the floor. Self-leveling mixtures spread on the floor independently, without human intervention. They include:
- gypsum or cement,
- fine sand
- plasticizers that improve quality indicators,
- glue,
- pigments.
Attention! The minimum and maximum thickness of the screed of a certain composition are indicated on the packaging by the manufacturer.
A bulk floor is a type of self-leveling mixture that is applied to a concrete base or cement-sand pouring. This compound is used as a topcoat or as a thin layer of screed from 2 to 20 mm.
Advice! For a bulk floor, the thickness is recommended no more than 20-30 mm: otherwise, it may crack with time.

Concrete remains an indispensable material for roughing, due to its relative cheapness. SNiPom recommended the following composition of the mixture:
- sifted sand
- cement,
- gravel or crushed stone (size of fractions from 5 to 15 mm),
- water.
Today, very often instead of gravel, lighter fillers are used, which also have thermal insulation properties. The most common of them are expanded clay and expanded polystyrene (granules). The first is used only as a component for pouring the rough floor, and the second - for the finish. The height of laying the mortar is in the range from 30 to 50 mm and is used in cases where there is a need to remove irregularities whose size is more than 20 mm.
With significant differences (more than 60 mm), sand concrete is used, which instead of ordinary sand includes coarse-grained sand. The height of this layer ranges from 100 to 150 mm.
In order to speed up the process of repairing the floor and in the presence of significant damage to the foundation, very often a dry screed is made, which includes materials that do not require drying for a long time. It includes a layer of backfill material, for example, expanded clay, and on top of a sheet material (particleboard, plywood, GVLV). If necessary, hydro-, heat- and noise insulation is carried out. The thickness of such a “pie” can be 35-60 mm.

What to consider when calculating layer thickness
Screed height affects floor performance. Too small a layer thickness will not provide sufficient sound insulation, heat saving and durability.
Excessive thickness will create additional load on the plate, which can lead to an emergency condition. For the durability of the coating and the rational consumption of materials, the optimum thickness of the concrete screed must be correctly calculated.
What you need to pay attention to when calculating:
- Functional purpose of the room.

- Materials used for mounting the floor base. If the concrete base is poured onto a heat-insulating layer, its thickness must be at least 4 cm.
- Plate condition. If it is located on a slope or has differences in height, then a thicker layer will have to be made. In case the height differences are small, the screed should be at least 2 cm, and filled using reinforced mesh to prevent cracking of the base.
- Finishing coat to be laid after screeding.
- If a warm floor will be mounted, in this case the thickness depends on the type of heating elements used.
When pouring a cement screed, you do not need to be guided by the principle "the thicker, the better." If the screed is mounted on a wooden base or soil, its thickness should be 4-5 cm.
If a warm floor with water heating is poured, then the screed is poured 3 cm above the pipes.
The disadvantages of the base of large thickness
 In the course of work, it should be borne in mind that too thick a layer has disadvantages:
In the course of work, it should be borne in mind that too thick a layer has disadvantages:
- high consumption of materials
- an increase in floor thickness leads to a decrease in the height of the room and an increase in the additional load on the stove,
- long drying screeds for the floor.
The thicker the concrete layer, the greater its expansion coefficient when exposed to high temperatures. If you do not provide the correct thickness of the expansion joint, the concrete base will expand on the walls during expansion, which will eventually lead to their deformation. When installing screeds without the use of reinforced elements, the thickness of concrete should be from 4 to 7 cm.
Functional purpose of the screed
The screed is mounted to compensate for differences in height, reinforces the concrete base and hides its defects.
Purpose of the sub floor:
- when we pour concrete, it fills the pores and microcracks in the slab, thereby increasing its strength and durability,
- a thicker layer within acceptable values contributes to the conservation of heat and is a barrier to the penetration of noise,
- a flat surface promotes easy installation of the finish flooring, protects it from damage when operating on an uneven base,
- when filling the floor, it is possible to provide for a technological bias in the kitchen and in the bathroom.
A topcoat laid on an even base will last longer and will look much more beautiful. If you lay linoleum on an uneven base, the flooring will crack over time, the joint locks on the laminate will diverge, the boards will creak and crack.
Types of screed
The type of screed is selected depending on the factors described above. To make a choice, consider the characteristics of all types of rough floors.
Types and characteristics of screed in the table:
| № | Type of screed | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Concrete | It is used to level the slab, poured with a solution of cement 1 part and sand 3 parts. We add dry components to water, mixes well. Dries up 28-30 days. |
| 2 | Using a self-leveling mixture | They are used for differences in height of up to 3 cm; the advantage is the ease of installation and drying of the base within 3-5 days. |
| 3 | Floating base | It is called so because the concrete layer is laid on the insulating material through a layer of plastic film, does not have adhesion to the slab. Thermal insulation is laid on a flat base, in order to avoid cracking of the thermal insulator. |
| 4 | Dry screed | It is used for differences in height of 3-5 cm, if the plate can not be loaded, performs the function of thermal insulation, is mounted using expanded clay, on which we lay the leveling materials. |
| 5 | Concrete screed, poured onto a layer of expanded clay | Significantly increases heat storage, reduces the load on the stove. |
When installing any type of foundation around the entire perimeter of the room, a damper summer must be glued along the wall, which acts as a compensation seam when expanding / narrowing the screed.
The thickness of the tape should be equal to the thickness of the base from the slab to the finish.
Prepare the stove
Preparation of the base is mandatory when installing the screed. This procedure includes several stages:
- We remove all peeling building materials from the floor, inspect for defects.
- We expand cracks with a width of more than 1 mm with a grinder, clean their edges from exfoliated concrete, remove dust, moisten abundantly, fill it with cement-sand mortar.
- After the cement has dried, we remove the building dust from the coating with a powerful vacuum cleaner (the presence of dust significantly reduces the adhesion of materials).
- We cover the surface with two coats of primer with an interval of application of 4 hours.
- On the perimeter of the room, glue the damper tape on the walls, which serves as a temperature joint during the expansion of the cement mortar during drying and protects the neighbors from below from water leakage during installation.
In private houses and on the first floors of high-rise buildings, to protect against moisture, we cover the slab with two layers of mastic based on bitumen or lay a plastic film.
We install beacons to determine the level of screed
To mark the boundary of the floor, we place beacons parallel to the wall at a distance of 150-200 mm. The step of laying the guide profiles should be slightly less than the length of the rule by which we distribute the concrete mortar.
As guides, we use profiles with a flat surface and expose them to a horizontal level. To install at the desired height, we use bars of materials resistant to moisture or we fix the beacons on a gypsum (cement) mortar.
At the end of the marking, we verify using the laser or bubble level the correct installation of beacons.
We prepare a solution
We are preparing a cement-sand mortar, for this we mix the dry components well with each other. Then we add water to about 400-500 ml of water per 1 kg of cement.
The solution should have a uniform consistency and look like thick sour cream. For surface plasticity and resistance to temperature extremes, special additives are added to the solution.
We choose the brand of cement according to the classification in the table
| Concrete grade | Application | Cement consumption in kg per 1 cubic meter of concrete |
|---|---|---|
| M 100 | It has low strength, suitable for concreting borders, fences that do not have bearing capacity | 165 |
| M 200 | It is most often used when installing the base of the floor, suitable for installation of foundations | 240 |
| M 300 | It has sufficient strength for the installation of foundations, ceilings, etc. | 320 |
| M 400 | It has the highest strength characteristics, it is used in the construction of load-bearing structures. | 417 |
Fill the screed
We begin the installation from the far corner of the room. During the execution of work, it is necessary to calculate the work so as to fill the floor without interruption.
To protect against cracking and increase the strength of the base, we reinforce the design with a thin metal mesh. The permissible thickness of the screed on the floor is from 2 cm on a flat surface and 4 cm on the insulation. Thicknesses of more than 7 cm can lead to a violation of the design of the plate.
Work sequence:
- Pour the prepared cement mortar between the beacons and stretch as a rule. By leveling the composition so that the solution is rammed and air bubbles come out of it. We make sure that voids do not form that reduce the density of the base.
- When the mortar is well set, but not yet dry, take out the guides, fill the voids with concrete, and then level it. More information about pouring screed on lighthouses:
The screed dries for about a month, depending on its thickness, temperature and humidity in the room. Gently walking on the base can be 4-5 days after the end of installation.
To prevent cracks in the screed, moisten it once a day by spraying it from the spray gun and covering it with polyethylene until it dries completely.
The device of the floor with a self-leveling mixture
Self-leveling mixtures are sold in bags, easily diluted with water and mixed without the formation of lumps. With differences in height of less than 3 cm, you can perform quick and easy do-it-yourself installation. This floor will dry in a week.
According to the instructions on the packaging, we dilute the mixture, mixing all the components well. Fill it on the prepared surface from the far corner, level it with a needle roller towards the entrance. Make sure that no air bubbles remain.
Installation of a floating base
Following the recommendations, you can install the floating screed yourself. For detailed instructions on pouring a floating base, see this video:
Installation sequence of the floating floor base:
- On the perimeter we glue the damper tape to the thickness of the screed.
- We lay the heat-insulating material only on a flat surface, the optimal raw materials are polystyrene foam boards.

- As a protection of thermal insulation from concrete penetration into it, we cover a thick plastic film, overlap the strips, isolate the joints with tape.
- We install beacons.
- We install a screed, while the minimum concrete layer should be at least 2 cm.
After the base has dried, we lay the finish flooring.
Dry coupler
Installation of any type of screed requires preparing the surface of the slab and marking the floor level.
- We mount the beacons at a distance of 150 cm, as supports for the height indicator we use linings made of dense material.
- Pour a layer of expanded clay to the top of the lighthouses, tamp it well so that there are no voids.
- The next step is to lay the sheet leveling material, which can be polystyrene foam, particleboard, fiberboard, plywood, gypsum or gypsum sheets. To better contact with the wall and prevent differences in height on sheets that are joined to the wall, we cut off the seam joints. The remaining sheets are joined together, smearing the seam side with glue, and in the end we additionally fix with screws.
- We take out the guides gradually as the plates are laid.
You cannot walk on the slabs before finishing work; we use material trimmings for movement.
Floor screed
What thickness will require a floor layer of screed depends on the type of heating elements.
For the installation of the base under the underfloor heating, special compositions are sold that are able to hold and retain heat well, since ordinary cement mortar can crack from heating.
When installing a water floor, the solution should cover the pipes by 30 mm, and when installing a cable heating system - by 20 mm. For detailed instructions on screeding underfloor heating, see this video:
The warm floor turns on after the screed has completely dried. If condensation has ceased to form on the plastic film that covers the coating, then the floor is ready for use.
 We examined what the screed should be in thickness and characteristics depending on the materials used. With the correct calculation of the optimal thickness of the screed, the base will serve for several decades without loss of quality.
We examined what the screed should be in thickness and characteristics depending on the materials used. With the correct calculation of the optimal thickness of the screed, the base will serve for several decades without loss of quality.
Using the described rules, you can easily perform installation of any kind of foundation with your own hands. The lifespan of the finish flooring largely depends on how smooth the surface is underneath.
Warm floor
When laying a warm floor, the following must be considered:
- The height (thickness) of the heating elements, which will subsequently be filled with the mixture. Based on the fact that the diameter of the pipes for such floors does not exceed 25 mm, the thickness of the concrete screed for a warm water floor will vary from 50 to 70 mm.

- We must not forget that the elements of the warm floor are heated, and, consequently, concrete, too. This leads to its expansion, and he, in turn, puts pressure on the walls, which can create an emergency.
- When we make a screed under the underfloor heating floor, do not make too thin a layer above the pipes, since in this case the heating of the surface will be uneven. But a very thick pouring layer (more than 50 mm) is also not recommended, as this leads to the fact that most of the thermal energy will be used to heat concrete. The optimum is a screed thickness of 40 mm above the pipes, and when using electric heating elements, 30–40 mm.





